Lemons and limes are two citrus fruits that have been used in culinary and medicinal practices for centuries. They are known for their tart and refreshing flavors, as well as their numerous health benefits. In this document, we will explore the botanical classification, physical characteristics, flavor profiles, nutritional content, culinary uses, medicinal properties, and geographic distribution of these two fruits.
Let’s dive in!
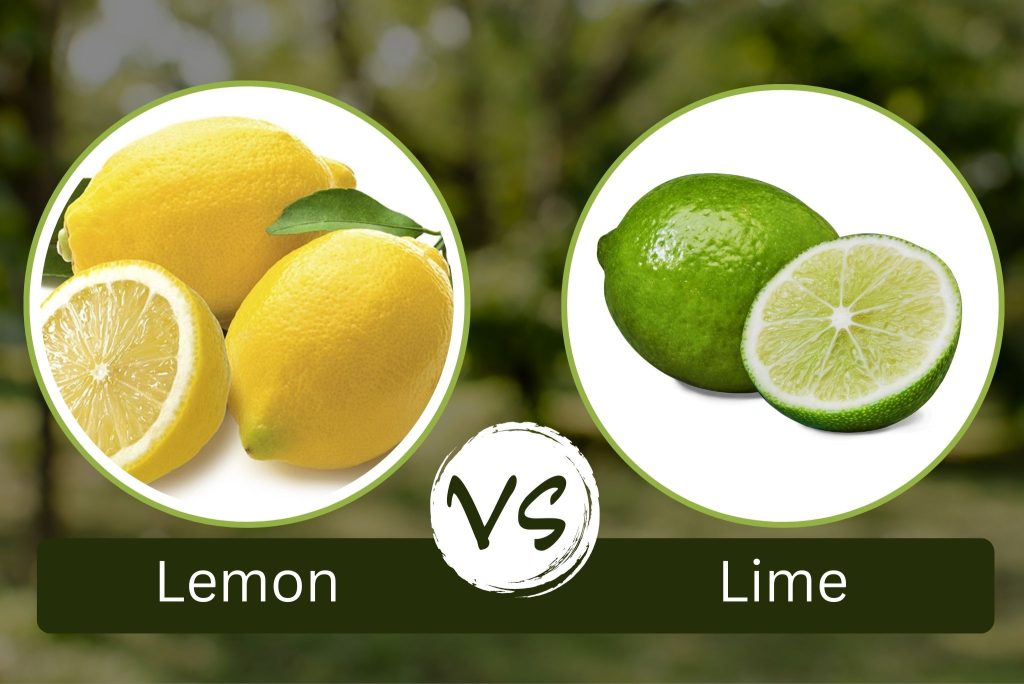
Botanical Classification
Lemon:
- Scientific name and family: The scientific name for lemon is Citrus limon and it belongs to the Rutaceae family.
- Origin and cultivation: Lemons are believed to have originated from Northeastern India, Northern Burma, and China. They were later introduced to European countries by Arabian traders. Currently, lemons are widely cultivated in warm and tropical regions around the world.
- Varieties: There are several different varieties of lemons, including Eureka, Lisbon, Meyer, and Verna.
Lime:
- Scientific name and family: The scientific name for lime is Citrus aurantifolia and it also belongs to the Rutaceae family.
- Origin and cultivation: Limes are said to have originated from Southeast Asia, but they are now grown in many tropical and subtropical areas including Mexico, Brazil, and India.
- Varieties: The most common varieties of limes are Key lime, Persian lime, Kaffir lime, and Finger lime.
Physical Characteristics
Lemon:
- Size, shape, and color: Lemons are typically oval-shaped with a bright yellow skin. They range in size from small to medium-sized fruits.
- Skin texture and thickness: The skin of lemons is rough and bumpy with a thick outer layer.
- Seed presence: Lemons usually have several small seeds scattered throughout the fruit.
Lime:
- Size, shape, and color: Limes are smaller in size compared to lemons and they have a rounder shape. They also have a bright green skin.
- Skin texture and thickness: The skin of limes is smoother compared to lemons and it is thinner with a glossy appearance.
- Seed presence: Limes have small, round seeds that are more concentrated towards the center of the fruit.
Flavor Profile
Lemon:
- Citrusy notes: Lemons have a strong and distinct citrus flavor that is both tart and acidic.
- Sweetness and acidity balance: They also have a balanced sweetness and acidity, which makes them a popular ingredient in many dishes.
- Aromatic qualities: Lemons have a strong and refreshing aroma that is often used in aromatherapy.
Lime:
- Citrusy notes: Limes also have a citrus flavor but it is slightly more bitter compared to lemons.
- Sweetness and acidity balance: Limes are known for their tart and acidic taste, but they also have a slight sweetness.
- Aromatic qualities: Limes have a strong and fresh aroma that is often used in perfumes and cosmetics.
Nutritional Content
Lemon:
- Vitamin C content: Lemons are an excellent source of vitamin C, providing over 40% of the recommended daily intake in just one fruit.
- Other vitamins and minerals: They also contain small amounts of other vitamins and minerals such as potassium, folate, and vitamin B6.
- Caloric content: One lemon contains around 17 calories, making it a low-calorie addition to meals and drinks.
Lime:
- Vitamin C content: Limes are also a great source of vitamin C, providing about 30% of the recommended daily intake in one fruit.
- Other vitamins and minerals: They also contain small amounts of potassium, folate, and vitamin B6.
- Caloric content: One lime contains around 20 calories, making it a low-calorie option for enhancing flavor in dishes and beverages.
Culinary Uses
Lemon:
- Culinary applications in cooking and baking: Lemons are a versatile ingredient that can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, from lemon cakes to lemon chicken.
- Beverages and cocktails: Lemon juice is a popular addition to drinks such as lemonade, tea, and cocktails.
- Preserving and pickling: The acidity of lemons makes them great for preserving foods like fruits, vegetables, and meats.
Lime:
- Culinary applications in cooking and baking: Limes are often used in Mexican, Thai, and Indian cuisine to add a tangy and bright flavor to dishes.
- Beverages and cocktails: Lime juice is a key ingredient in popular beverages such as margaritas and mojitos.
- Preserving and pickling: Limes are also used in pickling, especially in South American and Caribbean cuisines.
Medicinal Uses
Lemon:
- Health benefits and medicinal properties: Lemons contain antioxidants, which can help boost the immune system and fight against diseases.
- Traditional remedies: Lemon water is a popular traditional remedy for sore throats, indigestion, and detoxifying the body.
Lime:
- Health benefits and medicinal properties: Limes also contain antioxidants and are known to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Traditional remedies: In traditional medicine, limes are used to treat ailments such as constipation, nausea, and skin irritations.
Geographic Distribution
Lemon:
- Regions where lemons are commonly grown: Lemons are native to Asia but are now widely cultivated in warm and temperate regions around the world, including Spain, Italy, Greece, and California.
- Climate preferences: Lemons thrive in warm and humid climates, with temperatures ranging from 50-80°F.
Lime:
- Regions where limes are commonly grown: Limes are native to Southeast Asia but are now widely grown in tropical and subtropical regions such as Mexico, India, and Brazil.
- Climate preferences: Limes prefer warm and sunny climates with temperatures ranging from 75-85°F.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while lemons and limes may have some overlapping characteristics, there are also distinct differences between them. Lemons offer a bright and tangy flavor with a high vitamin C content, making them a versatile ingredient in both culinary and medicinal uses. Limes, on the other hand, have a more intense citrus flavor and are often used in Mexican and Southeast Asian cuisines. Both fruits have a long history of traditional use for various health benefits and play a significant role in the cuisine and cultures of many regions around the world. So next time you’re in the produce aisle, remember to choose between lemons or limes based on your desired flavor profile and culinary needs!
- Everything You Wanted to Know About Red Tamarillos - June 2, 2025
- A Guide to Tulips: Everything You Need to Know & More… - June 2, 2025
- Guanabana: Description, Flavor, Benefits, And Uses - May 27, 2025

5 thoughts on “Lemon vs Lime: Explore the Differences”
Comments are closed.